Description
what is a parallel pin?
Generally, parallel pins are designed for the fastening of two or more individual elements. A friction type connection can be achieved by the selection of suitable fits. If such connection is meant to be disconnected repeatedly, then it becomes preferable to use taper pins in accordance with DIN 1.
This parallel pin is used in the bottom of the V94.2 Turbine inner casing which must be manufactured of Strong stainless steel alloy and And this issue has been observed about this product. It is made of the X22CrMoV12 1(1.4923) material.
V94.2 Gas Turbine:
This turbine is built by Siemens. It has 162.1 MW nominal power and 50 Hz nominal frequency and is located at Kermanshah power plant, Kermanshah city of Iran. The stored data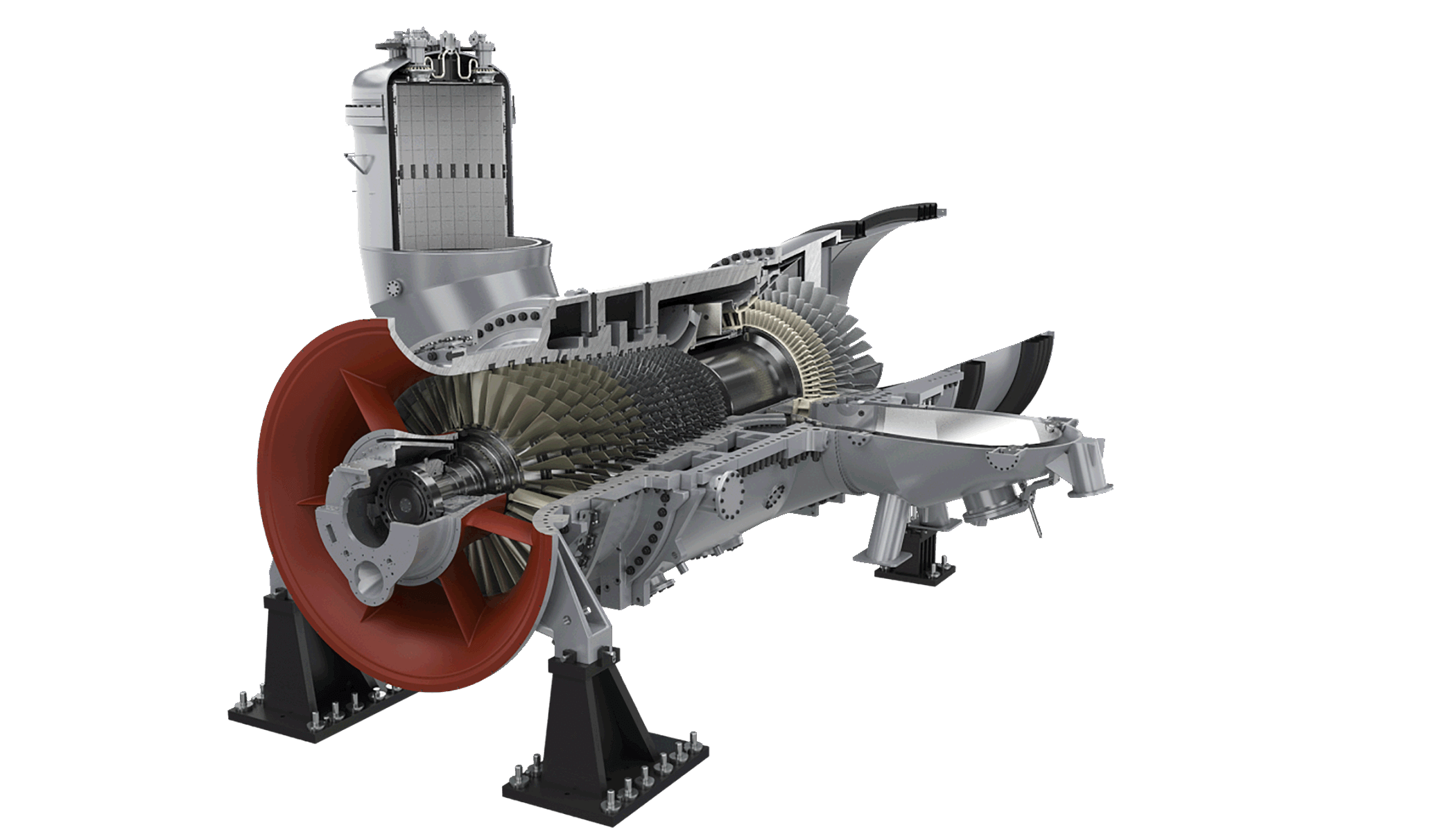
why parallel pin?
There are two common reasons for choosing parallel pin expansion. The first is that it could reduce the stress on tube seal welds. The second is that it is typically much faster than traditional expansion. Some end customers are requiring manufacturers to use parallel pin expansion on seal welded tubes. They believe this process can better protect the integrity of the weld. In traditional expansion, the feeding of the mandrel introduces a pulling force on the tube, thus creating stress at the weld. With parallel pin expansion this force could be reduced or eliminated since the mandrel is being pushed into the tube and the rolls are being forced directly outward towards the tube wall.














